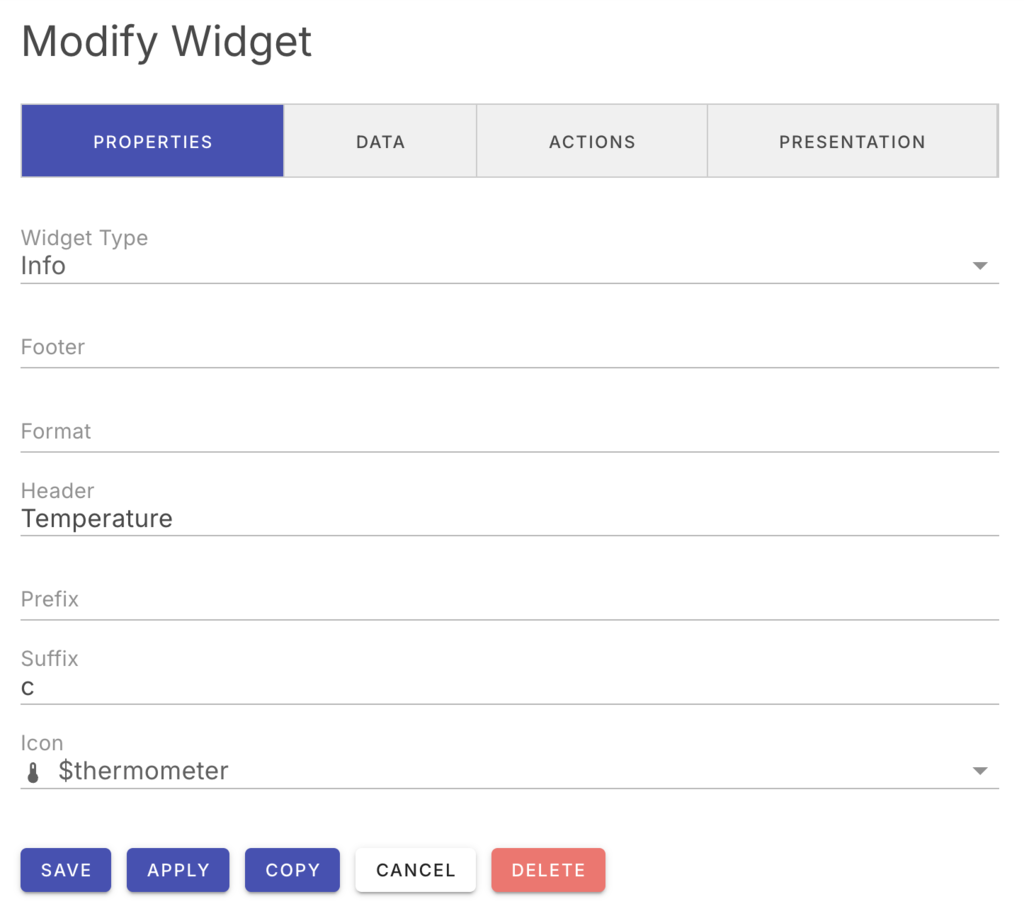
Metrics
For device data that is synchronized to the cloud, you can create custom metrics from the data stream. These metrics can then be displayed or graphed in the device app.
Ioto metrics automatically calculate statistics for the last "5 minutes", "hour", "day", "week" "month", or "year". For each timespan, you can query the average, minimum, maximum or sum value for the metric.
Metric Naming
Metrics are created and subsequently queried by a set of naming properties including:
- namespace
- metric name
- dimensions
The namespace is a global name to group related metrics. Currently, this must be set to Embedthis/Device.
The metric name is the specific metric name. For example: a device's temperature.
The dimensions select specific instances of a metric. For example, each device may have a temperature metric and we may also have an overall device pool average temperature metric.
Defining Metrics
In the process section for a model, define a metrics array of metric definitions. Each definition selects a data item value to be converted to a metric.
For example:
const DeviceSchema = {
process: {
Fault: {
sync: 'up'
metrics: [{
namespace: 'Embedthis/Device',
fields: [{Temperature: 'temp'}],
}]
}
},
...
}This will create a temperature metric from the item's temp attribute.
Metric definitions may contain the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| namespace | string | Metric namespace for the metric. Must be set to 'Embedthis/Device'. |
| fields | array | Array of metrics to create. Array metric entries may contain field attribute names or a map of a field attribute to a metric name. |
| where | string | Conditional expression to select items for which to create metrics. |
| buffer | map | Metric buffering directives. Defaults to null |
The metric namespace scopes the metrics and must be set to 'Embedthis/Device'. Other namespaces may be supported in the future.
The fields property contains an array with one or more metric definitions. Each definition may be either:
- An item attribute name which is used to identify the value AND to name the metric.
- A map of an item attribute name to a metric name.
For example:
{
fields: ['temperature', 'status', 'speed']
}This would create three metrics using the item's temperature, status and speed attributes. The metrics would take the same name.
Wheras:
{
fields: [{Temp: 'temperature'}, {Online: 'status'}, {Level: 'speed'}]
}This would create the metrics: Temp, Online and Level from the temperature, status and speed item attributes.
Where Expressions
The where property can be used to select matching items (rows).
The where query language is based on familiar Javascript expressions with some additional operators. Item attributes are expressed as variable names and literal values are expressed as JavaScript values.
For example: the expression:
error == "critical" && component == "PS1"
will select those items which have the error attribute set to "critical" and the component attribute set to "PS1".
For example:
{
ModelName: {
metrics: [
{
namespace: 'Embedthis/Device',
fields: [{CPU: 'value'}],
where: 'key == "cpu"',
}
]
}
}See Expressions for more information on the expression syntax.
Displaying Metrics
The device app can display metric data via graphical widgets
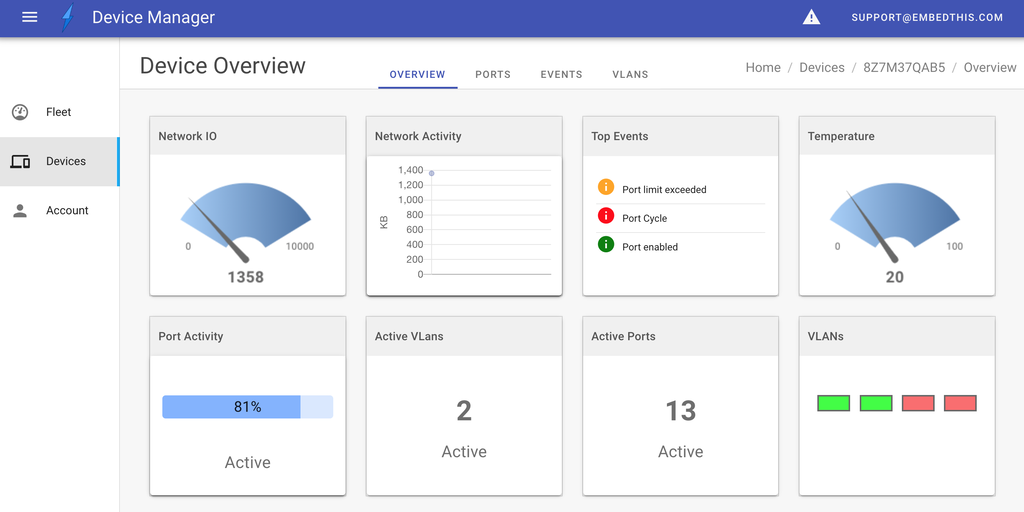
You can select from the following widget types:
- gauge
- graph
- table
- progress
- number
- leds
When creating or modifying a widget, you can select the data source to be either a database table item or a metric.
When selecting a metric, you enter the metric name, statistic and resource dimensions.
When selecting data directly from the database, you enter the database table model name, the model field (attribute) and a row selection expression.