IoT Automated Device Actions
When developing an IoT solution, it’s highly desirable to implement pre-programmed, automatic responses for when your devices or fleet encounter important conditions. Constantly monitoring every aspect of device status around the clock is impractical. By defining automated actions, you can enhance your device fleet’s intelligence, responsiveness, and availability.
Automated actions can transform your device cloud from a passive data repository into an intelligent, active and adaptive service. For example, automated actions can be used for the following scenarios:
- Invoke device actions in response to user input or measured device state.
- Compute device state to be reflected in the device app.
- Display device errors in an alert list in the device app.
- Aggregate fault metrics for devices and create dashboards for fleet health.
- Send alert email notifications to field staff for action.
- Integrate with systems and services from 3rd parties.
EmbedThis Ioto provides Automated Actions that can detect a wide variety of conditions and automatically initiate configured actions to alert or respond accordingly.
This post is the second of a series on the Ioto IoT cloud service. This post discusses automated actions. The other posts in the series are:
- Getting Started with Cloud-Based Device Management
- IoT Automated Device Actions
- Seamless Device Updates
Ioto Automations
EmbedThis Ioto enables automation via Actions and Alerts. Automation Actions monitor device and cloud states to evaluate data and determine if a predefined trigger condition is met. Automated Actions are invoked by condition triggers to respond and implement a specific remedy or notification. Alerts are a type of action that create human readable messages for display by the Builder console or device apps.
The EmbedThis Builder is used to create Actions that are deployed to the relevant device cloud and device apps. To create an Action, navigate to the Automations sidebar menu option and click Add Action.
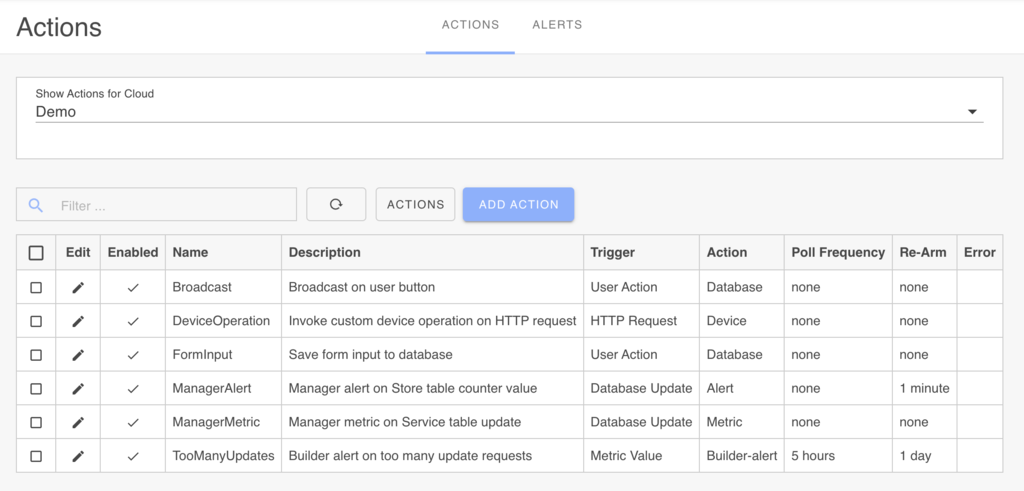
Condition Triggers
When creating an Action, you define the trigger condition that monitors to events, device or cloud state. Triggers can be defined for various sources, including device data, device metrics, cloud state, HTTP endpoints, or device app actions.
Three varieties of triggers are supported:
- Direct
- Streamed
- Polled
Direct triggers respond to user actions or HTTP requests to the device cloud endpoints. Streamed triggers monitor data as it is received by the device cloud from devices. Polled triggers run at a per-trigger frequency. This can be set to any number of minutes, hours, or days. While event triggers are run whenever the designated event is received by the Ioto device cloud.
| Trigger Source | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Database Value | Polled | Read a device database item value. |
| Metric | Polled | Monitor device and service metrics. |
| Database Sync | Event | Monitor synchronized device data that matches trigger expressions in the device schema. |
| HTTP | Direct | Respond to an incoming HTTP request. |
| User | Direct | Respond to a user command from a device app. |
See User Triggers for details about user device app actions and HTTP direct requests.
Matching Triggers
When a trigger event is received or polled, the associated trigger data is evaluated and compared with the Action’s trigger expression. If the expression evaluates to true, the trigger action is automatically invoked. For example, if you were polling a temperature field for a device, you could define a trigger expression to activate when the temperature exceeds 100 degrees.
Trigger Expressions
The trigger expression is a JavaScript like expression that is evaluated to yield a true or false result. If true, the Action is performed.
The trigger expression is supplied with a context of variables that can be accessed by the expression. The fields for a database item are provided as variables named for each field. For metric data sources, the metric result is provided as a “value” variable. For example:
value > 0
When triggers activate, they can pass additional parameters to the action to customize its behavior based on the specific trigger conditions.
Actions
When triggered, automation actions run to implement an appropriate notification or response action. Examples of automation actions include creating alerts, defining metrics, performing device operations, updating the device database and sending email notifications.
Action Types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Builder Alert | Create an alert in the Builder account |
| Builder Metric | Create a metric in the Builder account |
| Database | Create, update or remove an item in the device database |
| Device Command | Perform a device operation: release or reboot |
| Manager Alert | Create an alert in the device app account |
| Manager Metric | Define a device metric |
| HTTP | Invoke a HTTP REST API |
| Email* | Send an email message |
| Lambda* | Invoke a Lambda |
| MQTT Message* | Send an MQTT message |
| EventBridge* | Send an EventBridge event |
The Email, Lambda, MQTT and EventBridge actions require a dedicated device cloud.
Actions are configured with specific parameters to configure their operation. For example, an email action defines the email recipients, whereas an HTTP action defines the HTTP method, URL and HTTP headers.
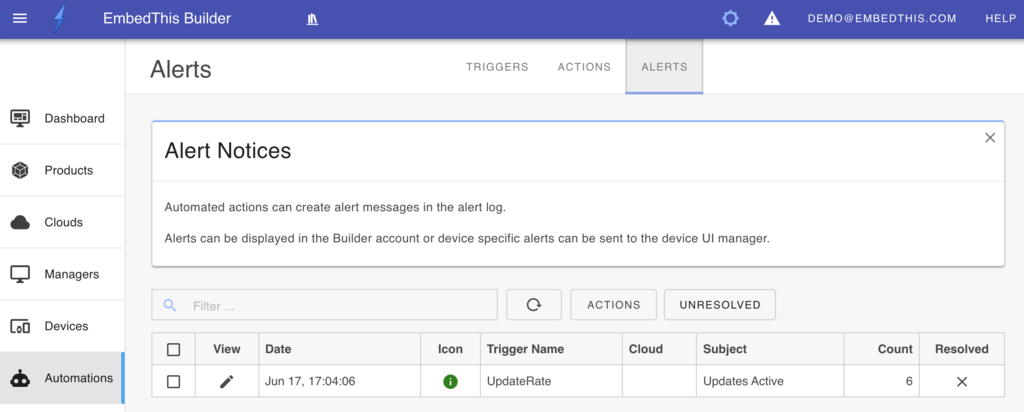
Alerts
Alert notices are a type of automation action. They can be created in both the Builder and device app using the Alert and Builder Alert actions. When paired with the appropriate triggers, these alerts offer convenient notification of alert conditions.
To prevent your alert inbox from becoming overwhelmed by repetitive messages, alert notices will aggregate repeated messages with identical content.
Device Commands
Devices are sometimes offline, either intentionally or due to transient network and infrastructure outages. So it is vital that device commands are reliably saved until they can be applied regardless of whether a device is offline or online at the time the command is issued.
To allow offline devices to receive commands, the Device Command automation stores commands in the cloud database and then distributes commands to one or more devices when they are online. If a device is offline, it will receive and respond to the command when it next connects to the cloud.
This is achieved by storing commands in the cloud-side database that is reliably replicated to the device when it next comes online — whereupon it runs all queued commands.
Rearming Delay
After a trigger has been activated and an associated action has been run, it can be useful to suppress further actions for a period of time. A rearm delay can be one or more minutes to suppress further triggers from activating.
Summary
To learn more, read about Automated Actions and get started with Builder Automations.
The next post will cover Seamless Device Updates.
Want More Now?
See what automations can do for you. Book a Demo
To learn more about EmbedThis Ioto, please read:
{{comment.name}} said ...
{{comment.message}}