Ioto on ESP32

The Espressif ESP32 is a low-cost, low-power system-on-chip (SoC) developed by Espressif Systems. It is widely used in embedded systems and IoT devices due to its versatility, strong performance, and integrated features.
Ioto brings to the ESP32 a new standard of IoT device management with transparent database synchronization to the cloud, a low-code app designer for mobile and desktop interfaces and unlimited metrics for extensive device metrics. Ioto is the leading IoT device management meta-platform for AWS.
This post details the steps required to build Ioto for ESP32 boards using the ESP IDF.
Please read the Building Ioto for general background first and Supported Hardware for a list of supported hardware.
Building Requirements
The Espressif ESP32 comes in many different varieties and flavors. Ioto will run on most ESP32 chips and has the following requirements:
- 256 KB internal RAM
- 2MB PSIRAM
Here’s a table summarizing the most common ESP32 chip variants, including the amount of RAM, number of cores, and supported PSRAM (external RAM):
| ESP32 Chip Variant | Cores | Internal RAM (SRAM) | Supported PSRAM | Ioto Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESP32 | 2 | 520 KB | Yes (up to 4 MB) | Yes |
| ESP32-S2 | 1 | 320 KB | Yes (up to 8 MB) | Yes |
| ESP32-S3 | 2 | 512 KB | Yes (up to 16 MB) | Yes |
| ESP32-C3 | 1 | 400 KB | Yes (up to 8 MB) | Yes |
| ESP32-S2FH | 1 | 320 KB | Yes (up to 8 MB) | Yes |
| ESP32-C6 | 1 | 512 KB | Yes (up to 8 MB) | Yes |
| ESP32-S3R8 | 2 | 512 KB | Yes (up to 16 MB) | Yes |
| ESP32-H2 | 1 | 256 KB | No | No |
| ESP32-PICO-D4 | 2 | 520 KB | No | No |
| ESP32-H2 | 1 RiscV | 320 KB | No | No |
Building Ioto for ESP32
This build sequence assumes you have your development environment setup on Linux or MacOS with the ESP-IDF installed. See ESP-IDF Setup for details.
To begin, open a terminal and create a directory for your project and the Ioto component. Choose any name you like for the project directory.
mkdir -p myproject
cd myproject
mkdir components
Next, add the ESP IDF PATH to your environment.
. ~/path-to-esp-idf/export.sh
Download Ioto
To download the Ioto device agent, navigate to the Builder site and select Products in the sidebar menu and click on the download link for the Ioto Evaluation.
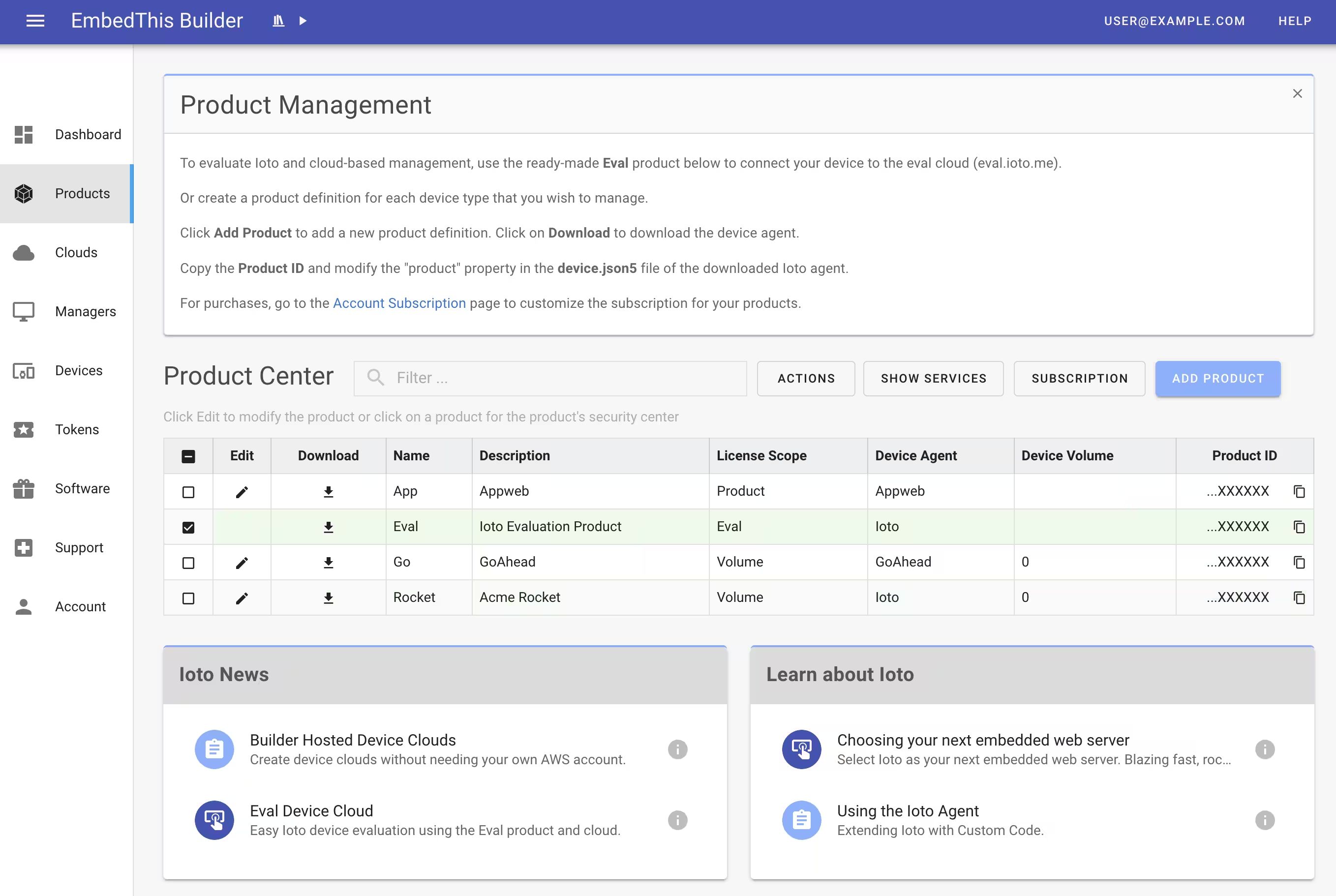
Extract the Ioto source code into the components directory. Then rename the ioto-VERSION directory to ioto.
cd components
tar xvfz ioto-VERSION.tgz
mv ioto-* ioto
cd ..
Sample apps
The Ioto source distribution includes several ESP32 example apps. Each example includes the necessary configuration files that are copied from the relevant app directory into build tree.
| Name | Directory | Description |
|---|---|---|
| esp32-blink | apps/esp32-blink | Blink a GPIO LED within the Ioto agent |
| esp32-dbsync | apps/esp32-dbsync | Create a demo counter and synchronize with the local and cloud databases |
The default app is the esp32-blink app which is ideal to test wheter you have ESP and Ioto successfully installed and configured. You can select an app by providing an APP=NAME option to the make command.
To prepare for building the app and Ioto, invoke make with your selected app.
make -C components/ioto esp32
or
make -C components/ioto APP=esp32-blink esp32
This command will perform the following steps:
- Create the esp32-blink app at main/main.c
- Create the app CMakeLists.txt
- Create the file system partitions.csv
- Create the app sdkconfig.defaults
- Initialize the components/ioto for the blink app
- Create some test certificates that may be required by the app
The components/ioto/apps directory contains master copies of the Ioto demonstration apps. When you select an app, the app code and configuration are copied to the ./main and ./fs directories.
Board Configuration
The next step is to ensure your ESP target device is defined. For example, to set the target to esp32-s3, invoke:
idf.py set-target esp32-s3
The default build configuration is defined via the sdkconfig.defaults file. You can tailor the configuration by running:
idf.py menuconfig
The Ioto services are enabled via the Ioto menu config option. Navigate to:
Components config --->
Ioto
then enable the desired services. This will update the fs/config/ioto.json5 and regenerate the sdkconfig and include/ioto-config.h files.
Check your sdkconfig that the following settings are defined:
| Key | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CONFIG_ESP_MAIN_TASK_STACK_SIZE | 8192 | Main task stack size (in words) |
| CONFIG_ESP_DEFAULT_CPU_FREQ_MHZ | 240 | CPU frequency setting to the fastest setting |
| CONFIG_ESP_DEFAULT_CPU_FREQ_MHZ_240 | y | CPU frequence alias |
| CONFIG_ESPTOOLPY_FLASHSIZE | 8MB | Flash memory size |
| CONFIG_ESPTOOLPY_FLASHSIZE_8MB | y | Flash size alias |
The full list is in components/ioto/apps/NAME/sdkconfig.defaults.
Building with idf.py
Building is performed via the ESP-IDF idf.py command instead of using the normal Ioto Makefiles which are used when building natively on Linux or MacOS.
To build for ESP32, run:
idf.py build
Update the Board Flash
To update your device with the built application:
idf.py -p PORT flash
Where PORT is set to the USB/TTY serial port connected to your device.
Monitoring Output
You can view the ESP32 and Ioto trace via the ESP32 monitor:
idf.py monitor
When running, the esp32-blink app will turn the LED On/Off every 2 seconds and trace the LED status to the monitor.
Local Management
If the selected app enables the embedded web server, files will be served from the ./site directory. The Ioto embedded web server is configured via the config/web.json5 configuration file which is then copied to the fs/config/web.json5 directory.
Tech Notes
The stack size is configured to be 32K for the main app task and for spawned fiber tasks. Observationally, the minimum stack for the core Ioto is ~14K.
Ioto uses its own optimized printf implementation which uses less stack (<1K) and is more secure, being tolerant of errant NULL arguments.
The PlatformIO and Arduino build environments are not (yet) supported.
{{comment.name}} said ...
{{comment.message}}